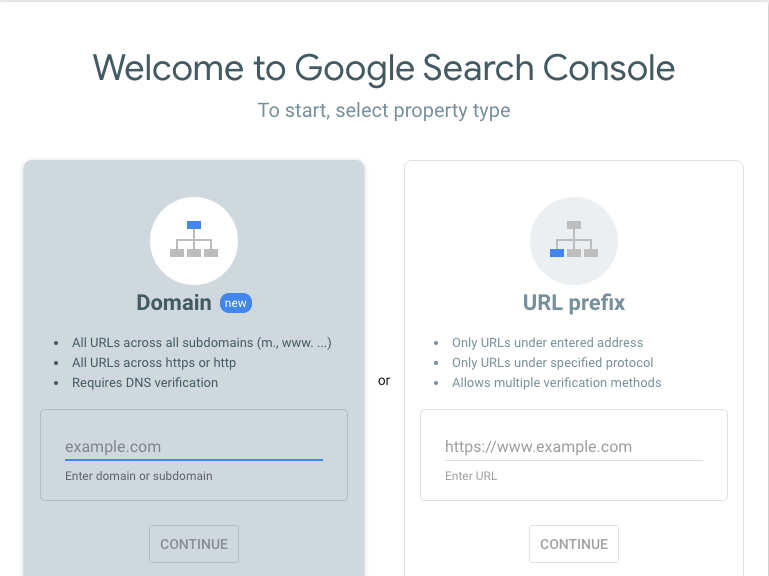
What is Google Search Console?

The Google Search Console, or GSC for short, is a service from Google Webmaster that allows you to access all sorts of information about the analytics and traffic to your website. In addition, you can use GSC to facilitate minor but impactful tweaks to your site. Google Search Console is like an SEO crystal ball for your website and allows you to see which of the pages on your site are the most popular amongst viewers; your relative statistics between mobile and desktop-based users; and your performance on the Google search engine. Best of all, Google Search Console is a free service!
Now that you know the basics of what Google Search Console is, the rest of this article will get you up to speed with all of the different functionalities and uses of this powerful tool. Stay tuned to turn your website game up to the max.
Google Webmaster Tools
As a history on the question What is Google Search Console? As an initial aside, Google Search Console used to be known by the name of Google Webmaster Tools, or GWT. Google Webmaster Tools was a long-standing service, offering pretty much the same functionalities as Google Search Console. Back in the day, many companies would hire webmasters to be in charge of their website functionalities.
However, in the modern-day, people in broader roles all use these services, from business owners and marketing specialists to software engineers and app designers. As such, in May 2015, Google updated the outdated name of Google Webmaster Tools to the more inclusive, current name of Google Search Console.
How to Submit a Website to Google Search Console
The first step to taking advantage of all of the functionality that Google Search Console has to offer is to submit your website to GSC. This first step consists of two distinct steps: adding your site to GSC, and verifying your site through GSC.
Once you have made an account on Google Search Console, log in to the GSC site. From there, you will be presented with an input box next to a red Add Property button. Select “website” from the available options in the drop-down menu, then enter your website’s URL in the box and click the button. This will take care of the first of the two steps discussed above: adding your site to Google Search Console.
Now that you have added your website to Google Search Console, you have to verify that this website belongs to you. This is because the powerful tools available through Google Search Console provide users with confidential information about site analytics, as well as control over how the site interfaces with Google’s various services. Allowing this information and authority to fall into the hands of a hacker or other undesirable owner cannot be allowed, hence the existence of this verification.
There are a variety of methods available to complete this verification process, which we will discuss below. Also, it is worth noting that verifying your website has no impact on its performance in PageRank or the Google search engine overall. For all of the following methods, begin by selecting “Manage property” and “Verify this property” for the appropriate site from the Google Search Console dashboard.
Option 1: Using an HTML tag. This is a simple way to verify your website, and a preferable one if you are familiar with using HTML code in website design. The Google Search Console will provide you with a string of HTML code you can copy—simply paste this code inside the Head section of your site’s HTML, then save and publish your site. Return to the Google Search Console dashboard and hit the Verify button. This method is a simple way of verification, as it informs Google that you have write access to the site in question.
Option 2: Uploading an HTML file. This method is similar to the HTML tag method, but Google Search Console will provide you with an entire HTML file, rather than just a string of HTML code. Download the GSC HTML file, then upload it to your site’s root directory, being sure not to change the file’s contents or name. As before, return to Google Search Console and verify your site once these steps are completed. It is important to note that, to remain verified and make use of Google Search Console’s services, you must ensure that the HTML file remains uploaded and unchanged in your site’s root directory. Failing to do so will cause your site to become unverified.
Option 3: Domain name provider. This is an excellent method for verification if you own a particularly large website for use with Google Search Console. Your domain name provider is the company that either hosts your website, or that sold you the domain name for your website in the first place. Enter your domain name provider’s title in the appropriate part of the Google Search Console verification tab, and GSC will guide you through how to create and verify a DNS TXT record through your provider.
Option 4: Using Google Analytics code. This is the preferable means of verification if your site already uses Google Analytics, or GA, to monitor site activity. Select this option from the GSC verification page, and follow the directions to verify your site. As an important note, the Google Analytics code must already be in the Head section of your site for this method to work. If it is in the Body section, simply cut and paste the code and proceed as described previously.
Option 5: Using Google Tag Manager. As before, this is an easy means to verify your website on Google Search Console if you already use the associated Google service. Ensure that you have View, Edit, and Manage permissions allowed for your Google Tag Manager (GTM) account, then follow the relevant instruction on the GSC verification page.
How to Submit a Sitemap in Google Search Console
Once you have added and verified your site on GSC, the next step is to submit a sitemap. Once you know how to submit a sitemap and submit website to Google Search Console, you will be well on the way to unlocking the functionality of this powerful tool.
A sitemap is a file that provides web crawlers and search engines, such as the Google ones, with key information about your site’s organization and variety of contents. Also, sitemaps can be packed with metadata, including details about digital and media content, as well as how often your site should be checked for changes to its content.
While adding a sitemap to Google Search Console is not an essential task, it does allow Google’s tools to function more efficiently and effectively. There are several cases in which uploading a sitemap is particularly important: if your site is new and not well linked to other sites and content; if your website is particularly large; or if your website contains a variety of pages that are not linked together very cohesively, we recommend that you take the time to upload a sitemap.
Once you have created a sitemap for your website, go to Crawl Sitemaps on the Google Search Console dashboard. Upload your sitemap by pressing the Add/Test Sitemap button, and you are all set!
Google Structured Data Testing Tool
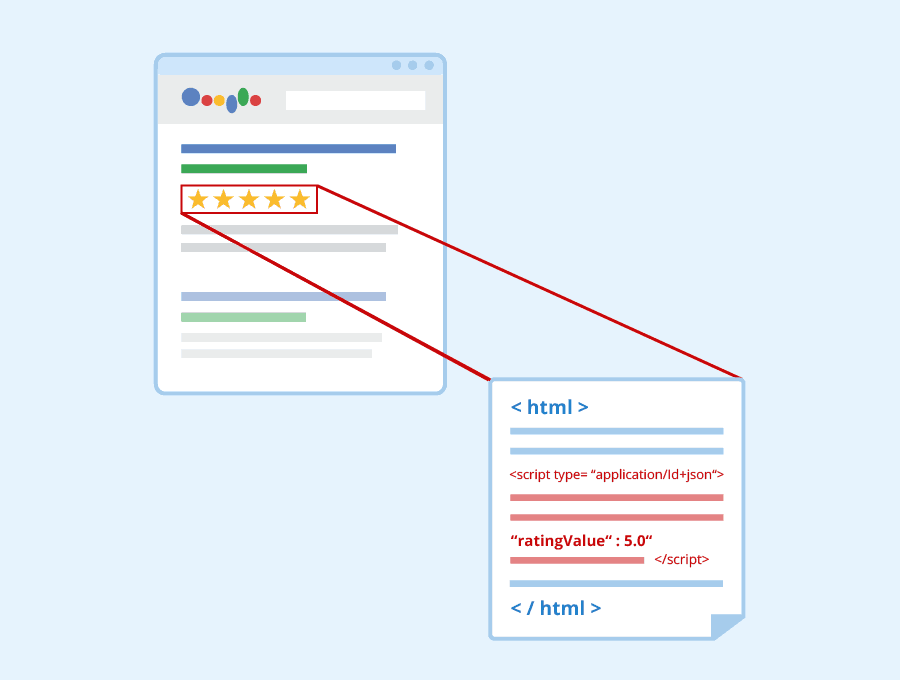
Structured data is a key part of many websites uploaded to Google Search Console. This denomination of data includes any information that is contained within a fixed field of a file, including databases, spreadsheets, and tables. While it is important, structured data is also prone to misinterpretation by the search engines crawling and ranking your site. Luckily, Google Search Console includes its very own tool to allow you to ensure that your data is being interpreted properly by computers as well as people.
First, navigate to the Google Structured Data Testing Tool, or SDTT, within the Google Search Console. On this page, enter the code that you want to test – the code that contains the structured data that you are concerned about. For certain data types, you will only be able to verify that your code can be interpreted by Google’s crawling services. However, if a Preview button pops up, that means you are working with a data type that can be visualized through the Structured Data Testing Tool. Pressing this button allows you to preview a sample search result based on your data, allowing you to see what people using Google search would see in the short snippet of information under your website’s title. It is this function of the Structured Data Testing Tool that leads some people to refer to this Google testing tool as the Google snippet tool.
Once you have verified that your data can be understood by Google’s crawlers, use the Google URL Inspection Tool, or UIT, for a better image of how Google’s systems see your website. To use the UIT, first ensure that you have set your page to be visible to Google, and that there are no gating obstacles that would prevent Google’s access to analyzing your structured data. Common examples of these obstacles include robots or login requirements.
Once you have confirmed that your webpage looks the way that you want it to through Google’s services, you can use the URL Inspection Tool to request an index of your webpage from Google. Indexing your webpage facilitates its processing through Google search and other Google services, and is an important step towards maximizing your site’s success.
Finally, once you have completed all of the steps up to this point, Google has a Rich Result Status Report Tool (RRSRT) which provides analytics of your website’s rich results, including structured data. To use this tool, your website should have multiple indexed pages, so ensure that you have done so before attempting to use the RRSRT. If the RRSRT reports little to no errors, while reporting improved rich result measurements, your structured data has been accepted properly! If this is not the case, you can iteratively update and test your structured data and results using the Structured Data Testing Tool’s previously discussed functionalities.
Once you have ensured that your structured data has been uploaded properly, you should still check in regularly using the Google Search Console to make sure that no future errors arise with future edits to your website’s code. Even if you update your site’s code in a way that shouldn’t impact your structured data, there is always the chance of a system-level issue arising. Generating and evaluating new rich result status reports with the Rich Result Status Report Tool is a valuable step to guaranteeing the long term health of your website.
Experimental Page Speed Tool
While Google Search Console is an incredibly useful service with many features and functionalities, the engineers at Google are constantly working to add more ways for the GSC to assist its users. One of the newest features rolled out as part of the Google Search Console is the experimental Page Speed Tool, or PST. First announced in February of 2019, this tool was released to the public in November 2019.
The Google Page Speed Tool presents an intuitive interface, grouping various URLs relevant to your website into categories of Slow, Fast, and Moderate. Furthermore, the PST can identify the root causes of slow website response in many cases. In these cases, it will group URLs with similar issues causing their slow responses, allowing you to solve and analyze these problems more efficiently. On the other side of the spectrum, the Page Speed Tool also allows you to explore the fastest URLs in your URL set, analyzing in exactly which ways these URLs are outperforming the rest.
The Google Page Speed Tool allows users to see the results of different edits and fixes to their websites in real-time. In addition, this tool allows users to have a broader, long-term perspective on the performance and improvements of their sites over time. This tool is incredibly valuable to the development of your website through Google Search Console, in terms of both the broad and the minute aspects of site design. The Page Speed Tool is currently designated as experimental by Google, as it is still under revision and will be improved with even further functionalities in the near future. Nonetheless, the Page Speed Tool is an excellent example of how Google is constantly rolling out improvements to the Google Search Console. Moreover, these improvements are not just small changes or ones with limited applications—tools such as the Page Speed Tool are widely applicable and highly valuable to any kind of Google Search Console user.
Fixing Mobility Usage Errors

In the modern-day, one up and coming field of website design is mobile site design—that is, ensuring that your website can be accessed equally easily from both desktop and mobile devices. With more and more people accessing the internet primarily from handheld or tablet mobile devices and the increasing popularity of mobile browsers, it is imperative that your site can be accessed without loss of quality or content from mobile devices. Luckily, Google Search Console can help with ensuring that any errors due to the transition from desktop to mobile website viewing are easily resolved.
As a first step, Google Search Console tells you which pages in particular on your website are causing issues and problems with usability when accessed from a mobile device. The Console’s Mobile Usability Report, or MUR, will intuitively single out whichever pages are above an allowable threshold of issues with mobile usability.
You can sort pages by their usability in this way; in addition, you can also sort by particular issues with usability. Common issues that Google will address include using plugins incompatible with most mobile viewing, such as Adobe Flash, not setting your viewport properly, making your text too small or your content too wide, or designing your website with interactive elements placed too closely together. Sorting by the issue will then tell you which pages on your website are affected by each issue. Furthermore, the Mobile Usability Report provides you with helpful information on how to fix each of these issues, as well as a means to inform Google about your process of fixing them.
This concludes our discussion of the most useful functionalities of Google Search Console. In this guide, we have discussed how to add a site to Google Search Console, how to validate sites on GSC, how to submit a sitemap to improve your site’s performance in Google services, how to test and validate your structured data, and how to address mobile usability errors through the Google Search Console. We also discussed how Google Search Console is an ever-improving service, with experimental tools such as the Page Speed Tool being added all the time.
Now, you should have a broad understanding of the different uses of the Google Search Console. By taking advantage of these GSC tips, you can propel your website to the next level!